The direct method is intuitive as it means the statement of cash flow starts with the source of operating cash flows. The operating cash out flows are payments for wages, to suppliers and for other operating expenses which are deducted. A cash flow statement (CFS) is a financial document that businesses use to measure incoming and outgoing cash and cash equivalents (CCE) over a set period of time. A cash flow statement is important for internal purposes, as it enables you to evaluate the financial health of your business and can help guide strategy. A CFS also serves an important purpose externally, like demonstrating your business’s ability to pay debts and expenses to potential investors or lenders. Since net income includes non-cash expenses under accrual-based accounting, you’ll need to add back any expenses that were reported but didn’t require an actual cash outflow during the period.
How to Calculate Depreciation Expense: Straight Line Method
Accounting practices, tax laws, and regulations vary from jurisdiction to jurisdiction, so speak with a local accounting professional regarding your business. Reliance on any information provided on this site or courses is solely at your own risk. For Example, if Accounts Receivable increases during the year – the company has sold more on credit during the year than it has collected in cash from customers. When an asset increases during the year, cash must have been used to purchase the new asset. Your balance sheet shows an original value of $15,000 and accumulated depreciation of $10,000.
Adjustment Three: Adding and Subtracting Changes in Current Assets and Current Liabilities
We accept payments via credit card, wire transfer, Western Union, and (when available) bank loan. Some candidates may qualify for scholarships or financial aid, which will be credited against the Program Fee once eligibility is determined. Please refer to the Payment & Financial Aid page for further information. Cash flow is typically depicted as being positive (the business is taking in more cash than it’s expending) or negative (the business is spending more cash than it’s receiving). Whenever you review any financial statement, you should consider it from a business perspective. Financial documents are designed to provide insight into the financial health and status of an organization.
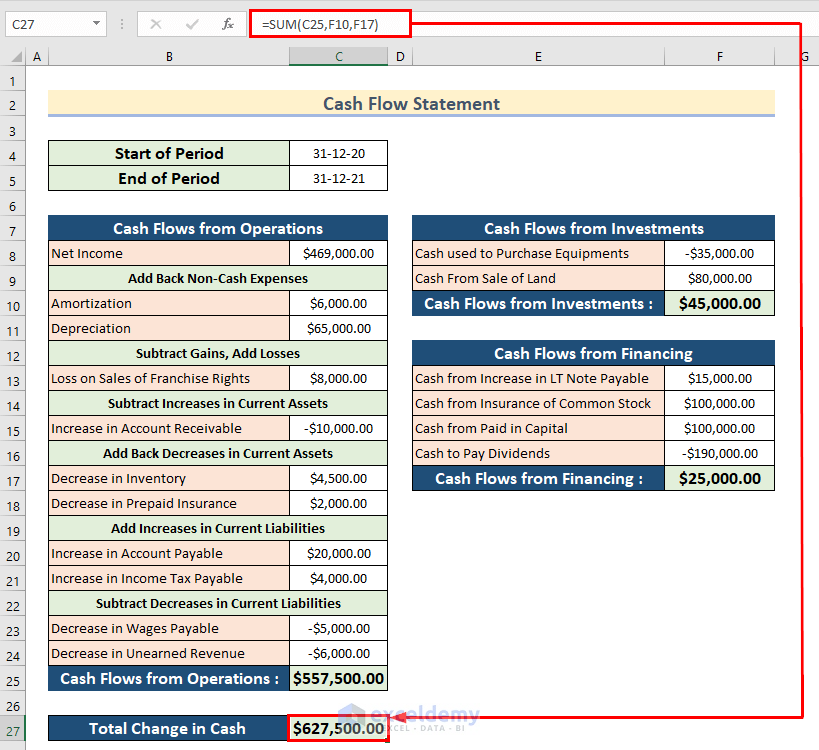
3 Prepare the Statement of Cash Flows Using the Indirect Method
The journal entry to record depreciation debits an expense account and credits an accumulated depreciation account. This transaction has no effect on cash and, therefore, should not be included when measuring cash from operations. Because accountants deduct depreciation in computing net income, net income understates cash from operations. Under the indirect method, since net income is a starting point in measuring cash flows from operating activities, depreciation expense must be added back to net income. An indirect cash flow statement is relatively simple to prepare, making it the ideal method for single business owners and small businesses as well as larger businesses with several moving parts.

4 BalanceUp is a discretionary overdraft program for debit card purchases only, offered for Lili Pro, Lili Smart, and Lili Premium Account holders; applicable monthly account fees apply. Once enrolled, your Account must remain in good standing with a deposit and spending history that meets our discretionary requirements to maintain access to the feature. BalanceUp overdraft limits of $20-$200 are provided at our sole discretion, and may be revoked any time, with or without notice.
Ask Any Financial Question
After reviewing its options, the company chose to give much of this cash back to shareholders in the form of cash dividends. A one-time increase in cash dividends resulted in $33,500,000,000 paid to the owners of the company during the second quarter of fiscal year 2005 (three months ended December 31, 2004). This information is found in the financing activities section of Microsoft’s statement 8615 instructions of cash flows. Items that are added or subtracted include accounts receivables, accounts payables, amortization, depreciation, and prepaid items recorded as revenue or expenses in the income statement because they are non-cash. The indirect method for calculating cash flow from operating activities begins with net income and adjusts for accrual impacts during the reporting period.
This increase in inventory would be reflected as a use of cash in the cash flow statement because it represents cash that has been invested in inventory rather than being available for other uses. Similarly, a decrease in current liabilities, such as a reduction in accounts payable, indicates that the company has used cash to settle its obligations, which also represents a use of cash. The indirect method’s reconciliation of net income to cash provided by operating activities is not complete without considering the changes in working capital. Working capital is the difference between a company’s current assets and current liabilities.
- This section covers cash transactions from all of a business’ operational activities, such as receipts from sales of goods and services, wage payments to employees, payments to suppliers, interest payments, and tax payments.
- In fact, you don’t even need to go into the bookkeeping software to create this report.
- Assume your specialty bakery makes gourmet cupcakes and has been operating out of rented facilities in the past.
- She wants to determine her cash flow using the indirect method and base it on last year’s finances.
For instance, if a company issues stock options to employees as part of their compensation, the related expense is recognized in the income statement, but there is no immediate cash outflow. In the cash flow statement, this expense is added back to net income since it does not consume cash. Investing activities include transactions involving the acquisition and disposal of long-term assets and investments. These can range from the purchase of machinery and equipment to the sale of securities or subsidiary companies. In the indirect method, cash flows from investing activities are listed separately from operating activities to provide clear insight into how a company is allocating its resources for long-term growth and maintenance. Typically, these transactions are presented as cash outflows for purchases and cash inflows for sales, offering a straightforward view of the company’s investment strategy and its potential impact on future revenue streams.
Since equipment is a noncurrent asset, cash activity related to the disposal of equipment should be included in the investment activities section of the statement of cash flows. Thus the $6,000 loss shown as a deduction on the income statement is added back to net income, and it will be included later in the investing activities section as part of the proceeds from the sale of equipment. In effect, we are reversing the $6,000 loss because it is not an operating expense. When preparing an indirect method cash flow statement, you’ll start with the net income reported on the income statement. Then, you’ll make adjustments for non-cash transactions that were made using the increases and decreases in balance sheet items over the period.
Although a book entry, Depreciation and amortization expenses DO NOT not represent real uses of cash and are added back to Net Income. But the Profits reported in the Income Statement are not always representative of the actual Cash that has come into the business when we use Accrual Accounting. Even though the Format above includes all the aspects that can impact the Cash Flow from Operations using the Indirect Method – you will only apply what is relevant to the company you are analyzing.

0 Comments